Reflexology for ringing in ears is a complementary therapy that targets specific reflex points, primarily on the feet, hands, and ears, to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and reduce the perception of tinnitus. By addressing underlying imbalances, it aims to alleviate the persistent auditory sensation.
Understanding Tinnitus and Its Complexities
Tinnitus, often described as a ringing, buzzing, hissing, or roaring sound in one or both ears, is not a disease itself but rather a symptom of an underlying health condition. It affects millions worldwide, significantly impacting quality of life for many. The subjective nature of tinnitus means its perception varies greatly among individuals, ranging from a mild annoyance to a debilitating presence.
What is Tinnitus?
At its core, tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of an external acoustic stimulus. It can be objective, meaning a doctor can hear it, though this is rare, or subjective, which is far more common, where only the individual perceives the sound. The sounds can be intermittent or constant, vary in pitch and intensity, and often worsen in quiet environments. While commonly associated with hearing loss, tinnitus can also arise from a myriad of other factors, making its management particularly challenging.
Common Causes and Types
The causes of tinnitus are diverse and can include exposure to loud noise, age-related hearing loss, earwax blockage, Meniere’s disease, otosclerosis, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, certain medications (ototoxic drugs), head or neck injuries, and cardiovascular conditions. Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression can also play a significant role, not just in exacerbating symptoms but potentially contributing to its onset. Understanding the potential root causes is crucial for effective intervention, whether through conventional medicine or complementary therapies like reflexology.
The Conventional Approach vs. Holistic Views
Conventional medicine often focuses on managing tinnitus symptoms through sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT), and sometimes medication. While these methods can be effective for many, they don’t always address the underlying systemic imbalances that holistic approaches, such as reflexology, seek to correct. Holistic views consider the body as an interconnected system, where symptoms like tinnitus might be manifestations of disharmony elsewhere, such as in organ systems, circulatory health, or energetic pathways. This comprehensive perspective is where reflexology offers a unique and complementary pathway to relief.
The Kidney-Ear Connection in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Reflexology
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a profound understanding of the body’s interconnectedness, a philosophy that resonates deeply with the principles of reflexology. In TCM, the kidneys are considered the root of life, storing essential Jing (essence) and governing various bodily functions, including hearing. This ancient wisdom provides a compelling framework for understanding how kidney health might influence the auditory system and how reflexology can be applied to restore balance.
TCM Principles and Ear Health
According to TCM, the ears are seen as the “orifice of the kidneys.” This means that the health and vitality of the kidneys directly impact the health of the ears and one’s hearing ability. When kidney energy (Kidney Qi or Kidney Jing) is deficient, symptoms such as tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, and vertigo can manifest. The kidneys are also linked to the bone marrow, brain, and nervous system, further explaining their crucial role in sensory functions. A strong Kidney Qi ensures good auditory function, while weakness can lead to auditory disturbances. This connection is not merely metaphorical; it reflects a deep understanding of energetic pathways and physiological functions.
Reflexology Points for Kidney Meridian
Reflexology works by applying pressure to specific points on the feet, hands, or ears that correspond to different organs and systems of the body. For the kidneys, the primary reflexology point is located in the arch of the foot, approximately halfway between the ball and the heel, on the sole. Stimulating this point is believed to help cleanse and strengthen the kidneys, promoting better energy flow and detoxification. Given the TCM connection, working on kidney reflex points is a cornerstone of reflexology protocols for tinnitus. Regular stimulation of these points aims to nourish the kidney essence, which in turn is believed to support and improve auditory health.
How Kidney Energy Imbalance Affects Auditory Function
A deficiency in Kidney Qi can lead to a variety of symptoms beyond just auditory issues. It might manifest as lower back pain, knee weakness, fatigue, poor memory, and even premature aging. When this vital energy is depleted, the ears, being its external manifestation, suffer. The sound of tinnitus associated with Kidney Qi deficiency often presents as a low-pitched hum or buzz, and it may be accompanied by a feeling of emptiness or a hollow sensation. Reflexology aims to replenish this vital energy, thereby supporting the natural function of the ears. By stimulating the kidney reflex points, practitioners seek to re-establish the energetic balance, potentially mitigating the auditory disruptions caused by kidney disharmony.
Addressing Neck Tension and Its Impact on Auditory Nerves
Beyond internal organ connections, physical tension, particularly in the neck and shoulders, can significantly contribute to or exacerbate tinnitus. The intricate network of nerves, muscles, and blood vessels in the cervical spine region directly impacts the auditory system. Reflexology offers a non-invasive way to release this tension and restore balance.
The Cervical Spine and Cranial Nerves
The neck houses several crucial structures that can influence ear health. The cervical spine protects the spinal cord, and numerous nerves that transmit signals to and from the head, including some cranial nerves involved in hearing and balance, pass through or originate in this area. Specifically, the auditory nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve) transmits sound and balance information from the inner ear to the brain. Compression or irritation of nerves in the neck, often due to muscle tightness or misalignment, can interfere with these signals, leading to auditory symptoms like tinnitus. Moreover, the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles in the neck can refer pain and sensory disturbances to the ear area when tight or spastic.
How Muscle Tightness Contributes to Tinnitus
Chronic tension in the neck and shoulder muscles can lead to a cascade of problems. It can restrict blood flow to the head and inner ear, deprive tissues of oxygen and nutrients, and irritate nerves. This physical stress can alter how the brain processes auditory signals, potentially leading to or worsening tinnitus. Many individuals report that their tinnitus intensity fluctuates with neck movements or changes in posture, indicating a clear musculoskeletal link. Reflexology aims to release this myofascial tension, thereby improving nerve function and circulation to the head and ears. This mechanical component of tinnitus is often overlooked but can be a significant contributing factor.
Reflexology Techniques for Neck and Shoulder Relief
In reflexology, the reflex points for the neck and shoulders are found along the base of the toes and the ball of the foot (specifically, the area below the toes on the top of the foot for the neck, and the fleshy part below the pinky toe for the shoulder). For hand reflexology, these points are mirrored at the base of the fingers and the fleshy part below the little finger. Applying sustained, gentle pressure and kneading motions to these areas can help relax tight muscles, improve circulation, and alleviate nerve compression. This can be particularly effective for somatic tinnitus, which is influenced by movement or touch in the head and neck region. Regular work on these points can help to reduce the physical stress that often accompanies, or even causes, the ringing in the ears.

Improving Micro-Circulation to the Inner Ear
Optimal blood flow is essential for the health and function of every organ, and the delicate structures of the inner ear are no exception. Poor micro-circulation can starve the tiny hair cells and nerves responsible for hearing, potentially contributing to the onset or persistence of tinnitus. Reflexology aims to enhance this vital blood supply.
Importance of Blood Flow for Auditory Health
The inner ear, particularly the cochlea, is highly vascular and requires a constant, rich supply of oxygen and nutrients to function correctly. The hair cells within the cochlea, which convert sound vibrations into electrical signals for the brain, are extremely sensitive to changes in blood flow. Any impairment to the micro-circulation—the flow of blood through the smallest vessels—can lead to cellular damage or dysfunction, manifesting as hearing loss, dizziness, and tinnitus. Conditions like atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or even prolonged periods of stress can compromise this delicate circulatory balance, directly impacting auditory health. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) highlights various vascular disorders that can cause pulsatile tinnitus, underscoring the critical role of circulation.
Reflexology’s Role in Enhancing Circulation
One of the primary theories behind reflexology’s effectiveness is its ability to improve overall circulation. By applying pressure to specific reflex points, practitioners believe they can stimulate the circulatory and lymphatic systems, encouraging better blood flow throughout the body, including to the head and inner ear. This enhanced circulation can deliver more oxygen and essential nutrients to the auditory structures while simultaneously aiding in the removal of metabolic waste products. The increased blood flow can help to revitalize fatigued cells, reduce inflammation, and improve the overall physiological environment of the inner ear, potentially alleviating tinnitus symptoms related to circulatory deficiencies.
Specific Reflex Points for Blood Flow and Oxygenation
To specifically target improved circulation for tinnitus relief, reflexologists often focus on a combination of points. Besides the kidney points mentioned earlier (which govern vitality and overall systemic health), key points include those for the heart (responsible for pumping blood), the adrenal glands (which influence blood pressure and stress response), and general circulatory points located throughout the feet and hands. The diaphragm reflex, found as a line across the ball of the foot, is also crucial, as stimulating it can promote deeper breathing, thereby increasing oxygen intake and circulation. Additionally, working on reflex points corresponding to the brain and head can directly support blood flow to these areas. By systematically stimulating these points, reflexology aims to create a systemic improvement in circulatory health, with a beneficial ripple effect on the inner ear and its intricate functions.
Stress Management for Tinnitus Spikes: A Reflexology Perspective
The relationship between stress and tinnitus is well-documented and often cyclical. High stress levels can initiate or worsen tinnitus, and conversely, the presence of tinnitus can be a significant source of stress. Breaking this cycle is crucial for effective tinnitus management, and reflexology offers a powerful tool for stress reduction.
The Tinnitus-Stress Cycle
Stress triggers the body’s ‘fight or flight’ response, releasing hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can increase blood pressure, muscle tension, and heighten sensory perception, making tinnitus sounds seem louder and more intrusive. Chronic stress can also impair the immune system and disrupt sleep patterns, further aggravating tinnitus. Individuals often report that their tinnitus spikes during periods of high anxiety, work pressure, or emotional distress. This creates a vicious cycle: stress makes tinnitus worse, and worse tinnitus causes more stress. Addressing the root of stress is therefore a vital component of holistic tinnitus relief.
Autonomic Nervous System Regulation
Reflexology is believed to influence the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls involuntary bodily functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. The ANS has two main branches: the sympathetic (fight or flight) and the parasympathetic (rest and digest). Chronic stress over-activates the sympathetic nervous system. Reflexology aims to shift the body into a more parasympathetic state, promoting relaxation and calming the nervous system. By doing so, it can help reduce the physiological responses associated with stress, such as muscle tension and heightened sensory perception, which can directly alleviate tinnitus severity. This regulatory effect on the ANS is a key mechanism through which reflexology can offer relief.
Calming Reflex Points for Anxiety and Stress
Several reflex points are particularly effective for promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. The solar plexus reflex, located just below the ball of the foot in the center, is often referred to as the “stress button.” Applying gentle, sustained pressure to this point can induce a profound sense of calm. Other important points include those corresponding to the diaphragm (to encourage deep breathing), the adrenal glands (to help regulate stress hormone production), and the entire spinal reflex (to soothe the central nervous system). Furthermore, working on points related to the brain (pads of the toes/fingers) and pituitary gland (center of the big toe/thumb) can help balance hormone production and promote mental clarity. Regular work on these calming points can help individuals better cope with stress, potentially leading to a reduction in tinnitus intensity and frequency. Research on reflexology and stress reduction often points to its ability to induce a relaxation response, which can be invaluable for tinnitus sufferers.
Practical Reflexology Techniques for Tinnitus Relief
While seeking a qualified reflexologist is ideal, understanding some basic techniques allows for self-application, empowering individuals to take an active role in their tinnitus management. Focus is typically placed on the feet, hands, and ears, as these areas host the most accessible reflex points.
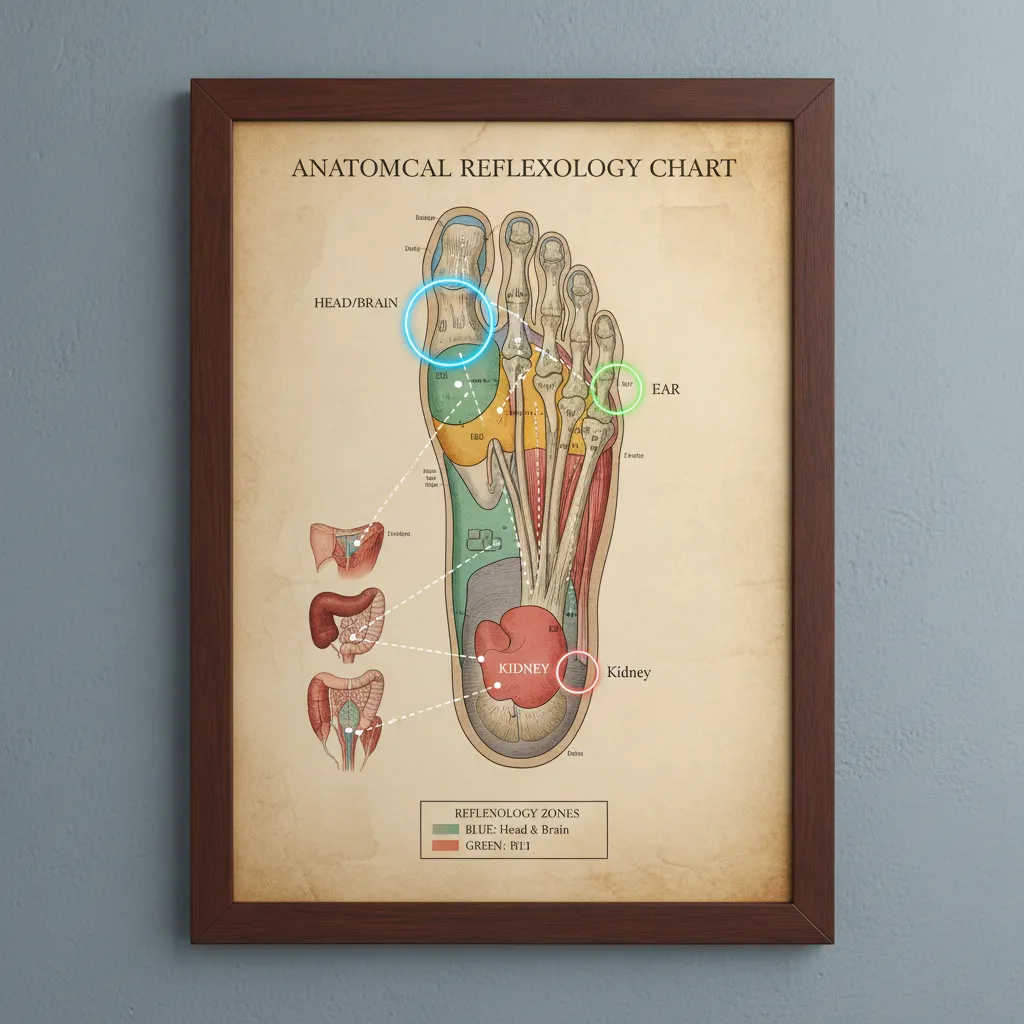
Foot Reflexology Zones for Ear and Head
- Toes: The tips of all toes, especially the big toe, correspond to the head and brain, including the frontal sinuses. Applying pressure here can help relieve congestion and improve circulation to the head.
- Ear Reflex: The reflex point for the ears is located at the base of the fourth and fifth toes on the sole of the foot. Gently press and rotate your thumb or finger into this area.
- Kidney Reflex: As discussed, the kidney point in the arch of the foot is crucial. Work this area deeply to support kidney energy.
- Neck and Shoulder Reflex: The base of all toes and the ball of the foot, particularly below the pinky toe, correspond to the neck and shoulders. Knead and stroke these areas to release tension.
- Solar Plexus: This central point just below the ball of the foot can provide overall relaxation and help calm the nervous system.
Use your thumb or fingers to apply steady, firm pressure, working in small circular motions or sliding strokes. Spend a few minutes on each area, listening to your body’s feedback.
Hand Reflexology for Self-Application
Hand reflexology offers a convenient alternative, especially when foot access is difficult or impractical. The reflex points mirror those on the feet:
- Fingertips: Correspond to the head and brain. Gently squeeze and massage each fingertip.
- Ear Reflex: Located at the base of the fourth and fifth fingers, mirroring the foot.
- Kidney Reflex: In the center of the palm, below the middle finger.
- Neck and Shoulder Reflex: The base of the fingers and the fleshy area below the pinky finger.
- Solar Plexus: In the center of the palm, often slightly below the thumb pad.
Use the thumb of one hand to work the points on the other hand. This can be done discreetly and effectively throughout the day.
Auricular (Ear) Reflexology Basics
Auricular reflexology, or ear reflexology, involves stimulating points on the ear itself. The ear is considered a micro-system of the entire body. While more complex systems exist, a basic approach for tinnitus can involve:
- Gently massaging the entire ear, from the lobe to the helix.
- Paying particular attention to the outer rim and the central hollow of the ear, as these areas often correspond to the head, brain, and internal organs.
- Using a gentle pinch-and-release motion along the ear’s cartilage.
Always ensure cleanliness and avoid excessive pressure, especially if the ear is sensitive. The aim is to stimulate, not to cause pain.
Integrating Essential Oils (Optional)
For an enhanced experience, certain essential oils known for their calming and circulatory benefits can be incorporated. Lavender, known for its relaxing properties, or frankincense, often used for inflammation, can be diluted with a carrier oil (like jojoba or almond oil) and applied to the reflex points before or during the session. Always perform a patch test first and ensure the oils are safe for topical use. This adds an aromatic and therapeutic layer to the reflexology practice.
What to Expect from Reflexology Sessions
Embarking on a reflexology journey for tinnitus relief involves understanding the process, from finding a qualified practitioner to managing expectations regarding outcomes.
Finding a Qualified Practitioner
It is paramount to choose a reflexologist who is certified and experienced. Look for practitioners who have completed accredited training programs and are members of professional reflexology associations. These associations often maintain directories of qualified members. During your initial consultation, discuss your tinnitus, medical history, and expectations. A good practitioner will explain their approach, discuss a treatment plan, and answer any questions you may have. While reflexology is generally safe, it’s wise to ensure your chosen practitioner has a solid understanding of complementary health practices and can work alongside any conventional medical treatments you are receiving.
Session Frequency and Duration
The frequency and duration of reflexology sessions can vary depending on the individual’s condition and the practitioner’s recommendation. Typically, initial treatments might involve weekly sessions for 4-6 weeks to establish a baseline and allow the body to respond. As symptoms improve, sessions might be spaced out to bi-weekly or monthly for maintenance. Each session usually lasts between 45 minutes to an hour, providing ample time for comprehensive work on various reflex points. Consistency is key in reflexology, as cumulative effects are often observed over time rather than instant cures.
Potential Benefits and Limitations
Many individuals report significant benefits from reflexology for tinnitus, including reduced perception of the ringing, improved sleep, decreased stress levels, and an overall sense of well-being. By addressing underlying imbalances in circulation, nervous system regulation, and organ function, reflexology aims to create an environment where the body can better manage or even reduce tinnitus symptoms. However, it is important to manage expectations. Reflexology is a complementary therapy and not a guaranteed cure for tinnitus. Its effectiveness can vary greatly from person to person, and it should be viewed as part of a broader holistic health strategy rather than a standalone solution. It may not eliminate tinnitus entirely, but it can significantly improve quality of life by reducing symptom severity and associated distress.
Integrating Reflexology into a Holistic Tinnitus Management Plan
For optimal and sustainable relief from tinnitus, reflexology is best integrated into a comprehensive holistic management plan. This involves considering various aspects of lifestyle, diet, and when to seek conventional medical advice.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing tinnitus. Alongside reflexology, incorporating regular stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or tai chi can amplify the calming effects. Ensuring adequate, quality sleep is paramount, as fatigue can exacerbate tinnitus. Limiting exposure to loud noises and protecting your ears with earplugs in noisy environments can prevent further damage. Regular, moderate exercise also supports overall circulation and stress reduction. Adopting a mindful approach to daily activities, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, and quitting smoking can all contribute positively to your body’s ability to heal and manage auditory symptoms.
Dietary Considerations
Diet can significantly impact inflammatory responses, circulation, and nervous system health, all of which are relevant to tinnitus. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids, can be beneficial. Reducing processed foods, excessive sugar, and high-sodium items is often recommended. Some individuals find that certain foods or additives (like MSG or artificial sweeteners) trigger or worsen their tinnitus, so keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers. Maintaining good hydration is also vital for overall cellular function and circulation.
When to Consult a Medical Professional
While reflexology can be a powerful complementary tool, it is not a substitute for medical diagnosis and treatment. It is crucial to consult with a medical doctor or an audiologist if you experience new or worsening tinnitus, especially if it’s accompanied by sudden hearing loss, dizziness, vertigo, or if it’s pulsatile (synchronized with your heartbeat). A thorough medical evaluation can rule out serious underlying conditions and ensure you receive appropriate conventional care. Reflexology can then be used in conjunction with your doctor’s recommendations to support your overall well-being and enhance your healing journey. Always inform your medical practitioner about any complementary therapies you are undertaking.
Conclusion
Reflexology for ringing in ears offers a promising avenue for relief, operating on the principle that by stimulating specific reflex points, the body’s innate healing mechanisms can be activated. From addressing the vital kidney-ear connection in TCM to alleviating neck tension, improving micro-circulation, and profoundly impacting stress levels, reflexology provides a multi-faceted approach to managing tinnitus. While not a definitive cure, its ability to reduce symptom severity, enhance relaxation, and improve overall well-being makes it a valuable component of a holistic tinnitus management strategy. By empowering individuals to take an active role in their health, reflexology stands as a testament to the body’s remarkable capacity for balance and healing.
People Also Ask About Reflexology for Tinnitus
What specific reflexology points are best for tinnitus relief?
For tinnitus relief, key reflexology points include the ear reflexes (located at the base of the fourth and fifth toes/fingers), kidney reflexes (arch of the foot/center of the palm), neck and shoulder reflexes (base of all toes/fingers and ball of foot/palm), and the solar plexus reflex (center below the ball of the foot/palm) for stress reduction. Additionally, points for the head and brain (tips of toes/fingers) are often worked to improve overall cranial circulation.
How often should I do reflexology for ringing in ears?
The frequency of reflexology sessions for ringing in ears varies depending on individual needs and the severity of symptoms. Initially, weekly sessions for 4-6 weeks are often recommended to establish a therapeutic effect. Once improvements are noted, sessions may be reduced to bi-weekly or monthly for maintenance. For self-application, working on points daily for 10-15 minutes can be beneficial, but always listen to your body and consult with a qualified reflexologist for a personalized plan.
Can reflexology completely cure tinnitus?
While reflexology can significantly reduce the severity, frequency, and distress associated with tinnitus for many individuals, it is not considered a definitive cure. Tinnitus is a complex condition with various underlying causes. Reflexology aims to support the body’s natural healing mechanisms, improve circulation, reduce.